Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) superfamily proteins are potent regulators of cellular development and differentiation. Nodal/Activin/TGF-β and BMP ligands are both present in the intra- and extracellular milieu during early development, and cross-talk between these two branches of developmental signaling is currently the subject of intense research focus.
The heart is one of the earliest differentiating organs, and heart development requires stepwise regulation dependent on the precise control of genetic networks, in which Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling regulates cardiomyocyte commitment Numerous lncRNAs are broadly expressed during early heart development, and these early development and tissue homeostasis lncRNAs are also known to be induced by the TGF-β family. However, whether and how lncRNAs participate in cross-talk between TGF-β and BMP signaling branches has not been documented.
On September 22, 2022, Qiaoran Xi’s research group in Tsinghua University published a research article in Nucleic Acids Research entitled “LncRNA-Smad7 mediates cross-talk between Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling to regulate cell fate determination of pluripotent and multipotent cells”. In this study, they showed that Nodal-SMADs induces lncRNA-Smad7 transcription to regulate cell fate determination via repression of BMP signaling in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Depletion of lncRNA-Smad7 dramatically impairs cardiomyocyte differentiation in mESCs. Moreover, lncRNA-Smad7 represses Bmp2 expression through binding with the Bmp2 promoter region via (CA)12-repeats that form an R-loop. Importantly, Bmp2 knockdown rescues defects in cardiomyocyte differentiation induced by lncRNA-Smad7 knockdown. Hence, lncRNA-Smad7 antagonizes BMP signaling in mESCs, and similarly regulates cell fate determination between osteocyte and myocyte formation in C2C12 mouse myoblasts. Moreover, lncRNA-Smad7 associates with hnRNPK in mESCs and hnRNPK binds at the Bmp2 promoter, potentially contributing to Bmp2 suppression. The antagonistic effects between Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling via lncRNA-Smad7 described in this work provides a framework for understanding cell fate determination in early development.
Associate Prof. Qiaoran Xi from the School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University is the corresponding author of this article. Dr. Xiaohui Kong is the first author. Dr. Kun Yan, Dr. Haipeng Fu, and Hongyao Sun from Qiaoran Xi Lab, post-doc Pujuan Deng from Assistant Prof. Jun-jie Gogo Liu lab, post-doc Wenze Huang from Associate Prof. Qiangfeng Cliff Zhang Lab from the School of Life Sciences in Tsinghua University, Associate professor Shuangying Jiang from Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology in Chinese Academy of Sciences provided an important contribution to the study. This work was supported by NSFC grant and CLS program.
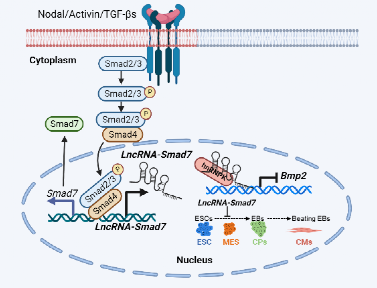
Working model of lncRNA-Smad7 in cross-talk regulation of TGF-β and BMP signalings (Figure was created in BioRender.com). The antagonistic effects between Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling via lncRNA-Smad7 described in this work provides a framework for understanding cell fate determination in early development. Nodal induced lncRNA-Smad7 represses Bmp2 expression through binding with the Bmp2 promoter region via (CA)12-repeats that form a R-loop. Moreover, lncRNA-Smad7 associates with hnRNPK in mESCs and hnRNPK binds at the Bmp2 promoter, potentially contributing to Bmp2 suppression.
Link: https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/nar/gkac780/6711145
